miRNA-Seq Analysis
miRNA-Seq, gene product abundance and discovery.
A microRNA (abbreviated miRNA) is a small single-stranded non-coding RNA molecule (containing about 22 nucleotides) found in plants, animals and some viruses, that functions in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRNAs function via base-pairing with complementary sequences within mRNA molecules. As a result, these mRNA molecules are silenced, by one or more of the following processes: (1) cleavage of the mRNA strand into two pieces, (2) destabilization of the mRNA through shortening of its poly(A) tail, and (3) less efficient translation of the mRNA into proteins by ribosomes. (Definition from Wikipedia: microRNA) [1]
Short description of the workflow and its purpose:
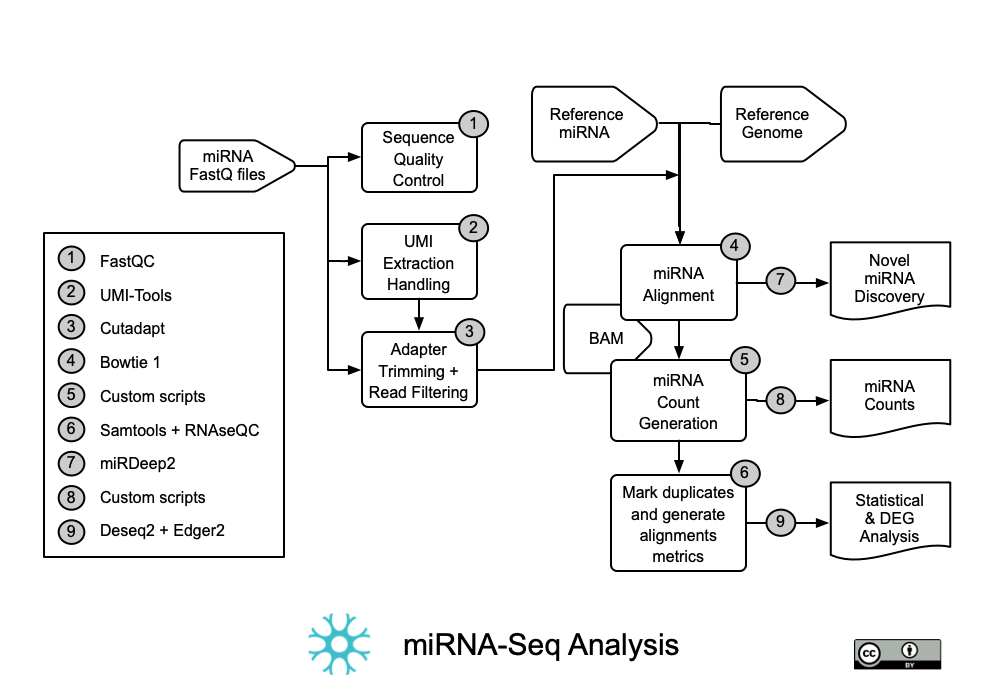
This workflow takes as input miRNA sequence reads (presumably with Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs)) in FASTQ format and uses a number of tools to QC, trim, map, analyze, count and do a differential gene expression depending on your experimental design. All of these tools and workflow were extracted from the Potlaab and colleagues publication[2]. Other details on Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data are also described in the publication from Fu and Dong [3].
Tools used in this workflow:
a. Fastqc
b. UMI-tools
c. Cutadapt
d. Bowtie1
e. Custom scripts [1]
f. Samtools + RNAseqc
g. miRDeep2
h. Custom scripts [3]
i. Deseq2 + Edger2
Bibliography:
- Wikipedia entry for microRNA: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MicroRNA
- Pratibha Potlaab, Shabana AmandaAli, Mohit Kapoor A bioinformatics approach to microRNA-sequencing analysis https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266591312030131X
- Bioinformatic Analysis of MicroRNA Sequencing Data. Fu X, Dong D. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1751:109-125. PMID: 29508293 and as a PDF on ResearchGate