RNA-Seq and Differential Expression Gene Analysis
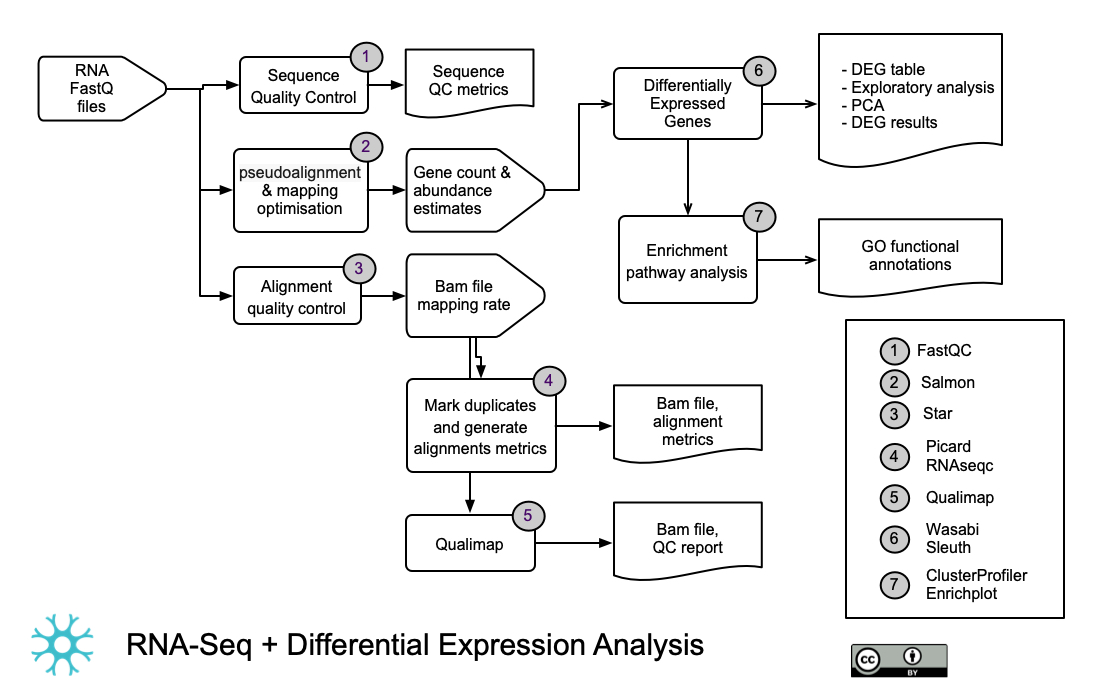
RNA-Seq, genes abundance and differential expression.
Understanding what transcriptome is present in a tissue or cell type is crucial to any functional genomic analysis, and many reviews on the topic of measuring RNA with next-generation sequencing technology abound [1].
Here is one protocol we have used at the Neuro: there are many others, and we encourage you to discuss alternatives with us.
Short description of the workflow and its purpose:
- This workflow takes as input RNA sequence reads in FASTQ format and uses Salmon to perform a “pseudo-alignment.” Pseudo-alignment consists of k-mer matching reads against a de Brujin graph of a transcriptome reference and quantifying the expression of transcripts.
- Transcript quantification and variance estimation are generated by bootstraps sampling and modelling sample-specific parameters and biases using a Variational Bayesian EM algorithm [2].
- Salmon quantification files are used as input for Sleuth differential expression analysis (DEG). In order to test for differentially expressed genes, Sleuth models the true biological variance using a general linear model and the technical variance generated by bootstraps sampling from pseudo-alignments [3].
- Original Link where workflow was first identified
- Original Link if a similar workflow exists in GenPipes (using kalisto) [4]:
- Workshop notes from the Griffith lab at Wash U (St-Louis): Intro to RNAseq Analysis
Bibliography:
- RNA sequencing: the teenage years. Stark R, Grzelak M, Hadfield J. Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Nov;20(11):631-656. PMID: 31341269
- Alignment and mapping methodology influence transcript abundance estimation. Srivastava A, Malik L, Sarkar H, Zakeri M, Almodaresi F, Soneson C, Love MI, Kingsford C, Patro R. Genome Biol. 2020 Sep 7;21(1):239. PMID: 32894187
- Differential analysis of RNA-seq incorporating quantification uncertainty. Pimentel H, Bray NL, Puente S, Melsted P, Pachter L. Nat Methods. 2017 Jul;14(7):687-690. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4324. Epub 2017 Jun 5. PMID: 28581496
- GenPipes: an open-source framework for distributed and scalable genomic analyses. Bourgey M, Dali R, Eveleigh R, Chen KC, Letourneau L, Fillon J, Michaud M, Caron M, Sandoval J, Lefebvre F, Leveque G, Mercier E, Bujold D, Marquis P, Van PT, Anderson de Lima Morais D, Tremblay J, Shao X, Henrion E, Gonzalez E, Quirion PO, Caron B, Bourque G. Gigascience. 2019 Jun 1;8(6):giz037. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz037. PMID: 31185495